Enterprise Resource Planning Systems: Everything You Need to Know

As businesses grow, organizing functions and data becomes more complex. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems provide a solution.
This guide has all you need to know about ERP systems, from the basics to the essential steps for successful implementation.
What Is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are software that streamlines a company’s operations. They let you automate critical aspects of your business, such as finance, inventory, and customer service.
ERP systems allow a company to keep all of its data in one centralized place. They also help manage the interactions among different departments, such as accounting, HR, sales, marketing, production, and supply chain management.
Keeping track of important data from different departments can take time and effort. But enterprise resource planning software makes it easier. These systems help organize data while ensuring that it’s accurate and easily accessible. As a result, companies can streamline their operations and become more efficient.
What Are the Characteristics of Enterprise Resource Planning Software?
You can distinguish ERP systems from other business software through the following characteristics:
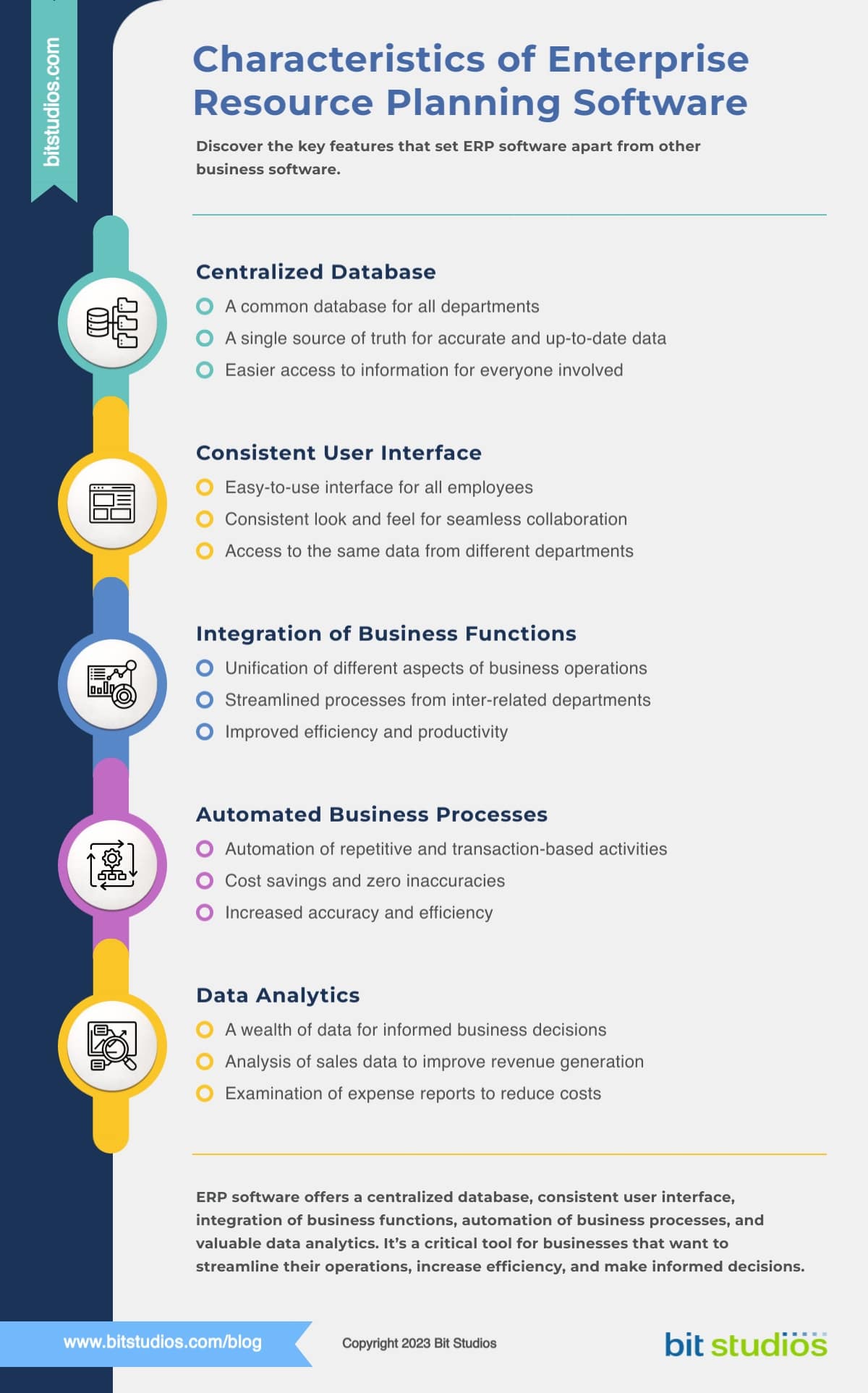
Centralized Database
An ERP system allows a company to establish a common database. Even if departments work independently and interconnectedly, they can rely on a single source of truth (SSOT).
Instead of combining multiple databases from different departments, a company can use a centralized database to access all the necessary information. This means the data is always accurate and up-to-date, making it easier for everyone involved.
Consistent User Interface (UI)
It is common for multiple departments and employees with different roles to have access to an ERP system. Because of this, ERPs typically come with an easy-to-use user interface (UI).
A consistent look and feel are also critical. This allows staff from different departments to access and understand the same data from the ERP and work together. With a consistent UI, collaboration becomes effortless.
Integration of Business Functions
An ERP system unifies different aspects of your business operations. You can integrate processes from inter-related departments like accounting and finance or sales and marketing.
Automated Business Processes
ERPs also let you automate specific business processes, especially repetitive tasks. These include transaction-based activities like invoicing or order processing and administrative functions like payroll or reporting.
Automation via ERPs can save you time and eliminate inaccuracies due to human error or duplicate entries.
Data Analytics
ERP systems are endless pools of data. You can leverage this wealth of information to improve different aspects of your business.
A classic example is examining sales data to check which areas of your business generate revenues. You can also look into expense reports to identify which costs you can reduce to make your operations more efficient.
Pros and Cons of Each ERP System Deployment Model
There are different types of ERP system development models. They can vary depending on your company’s exact nature and specific business needs.
On-Premises ERP: A Tried and Tested Model
In this model, you deploy the ERP system on your servers. You are also responsible for the security and maintenance of the ERP platform.
Pros of On-Premises ERP
- You have complete control over how to run and maintain the ERP system.
- You don’t need to ask permission from the ERP vendor when modifying your system.
- You are free to customize the ERP system according to your needs.
- On-premises ERP systems can offer more robust security, which is ideal if you require high intellectual property (IP) protection.
- You can run the ERP system without an Internet connection. If your systems go offline, your business functions and production process can continue.
Cons of On-Premises ERP
- Deploying on-premise ERP systems requires initial upfront costs compared to other ERP deployment models.
- If your company does not have the technical IT expertise, you will find it difficult to set up an on-premise ERP on your server. You will likely need to undergo additional training or hire a specialized skill set. Either way, you will be dealing with extra costs.
- If you haven’t fully backed up your ERP system, you can lose data if your server encounters issues. Fixing those issues and retrieving lost data can prove costly for your business.
- In-house ERP system deployment also means that you are shouldering all the server and hardware maintenance. Not to mention the added costs of backing up your data, setting up a cooling system for your server, and employing an IT team.
Cloud-Based ERP: Moving to the Cloud
This approach leverages cloud computing technology to set up the ERP system. Specifically, it involves deploying the ERP on remote servers managed and maintained by a cloud solutions provider. There are two types of cloud-based ERP deployments.
Hosted Cloud ERP Solutions
In this option, you acquire a license to use a cloud ERP system and then run it on rented remote servers managed by a hosting company.
Service providers typically label hosted cloud solutions as single-tenant setups. In this setup, you use a private cloud to store your data, and this cloud infrastructure is exclusive to you, not shared with other users.
True Cloud ERP Solutions
This setup involves paying for access to an ERP system that you can choose to manage or not.
An excellent example of true cloud deployment is a software-as-a-service (SaaS) ERP solution. You pay a fee to use the SaaS ERP, but the vendor typically maintains the ERP system.
Vendors often call true cloud setups multi-tenant solutions because other companies may also use the same ERP software.
Pros of Cloud-Based ERP
- It’s not as expensive as on-premise ERPs because you only pay a fee for the cloud service. Moreover, you don’t have to spend on hardware.
- Maintenance is easier because the vendor is usually responsible for the ERP system’s hardware and software upkeep.
- You can do away with the costs of maintaining the ERP and hiring an IT team.
- You can access the ERP system anywhere and anytime with an Internet connection and a compatible device. Cloud-based ERP is ideal for companies with multiple office locations or remote employees.
- Service providers typically have automated backup systems to protect your data in case of disasters.
- Cloud-based ERP systems are more scalable than on-premise ERPs.
Cons of Cloud-Based ERP
- You can’t use the cloud-based ERP if you’re offline. If you have an Internet connection, but it’s unreliable, it will likely affect how you operate the ERP’s UI.
- It’s not as customizable as on-premise ERP systems.
- If you have sensitive data, you may not be comfortable with entrusting it to a third party.
Hybrid ERP System Deployment Model
A hybrid ERP system combines the best of on-premise ERPs and cloud-based ERPs. There is no strict approach to a hybrid ERP deployment. Depending on your needs, you can borrow an on-premise ERP practice and pair it with a cloud-based strategy.
For example, you can set up an on-premise ERP system at your main headquarters office and then use cloud-based ERPs for other smaller office locations. Or you can have a primary on-premise ERP setup for core business functions and deploy cloud-based ERPs for specific operations.
Pros of Hybrid ERP
- It can be more cost-effective to purchase a cloud ERP system license for smaller office locations than extending a single on-premise ERP across all your branches. There’s no telling how IT infrastructure and personnel costs can add up in each site.
- If smaller office locations have specific local market needs, a hybrid ERP system is ideal. It is more flexible and faster to set up.
- Its deployment is less complex because you’re setting it up for a smaller office location, which tends to have simpler business functions than headquarters.
Cons of Hybrid ERP
- Combining on-premise ERPs with cloud-based ERPs can pose challenges in integration.
- You may incur additional costs in hiring experts to oversee the hybrid ERP system deployment.
- Security is a major concern when dealing with both on-premise and cloud-based ERPs. You have to consider each system’s security requirements and how they work together to ensure the overall protection of data and resources. Addressing both issues can be complex, requiring time and expertise to achieve optimal results.
Open-Source ERP Solutions
An open-source ERP system is available as free downloadable software. But beware that other open-source ERP service providers may charge a fee for cloud hosting.
Pros of Open-Source ERP
- It is cheap and, in some cases, free of charge.
- Some platforms come with active user community support, so you can request assistance to deal with standard deployment issues.
- You can customize open-source ERP systems according to your specific business needs.
Cons of Open-Source ERP
- You will likely handle most of the configuration and maintenance. It’s not surprising, given that you practically get the ERP system for free (mostly).
- Not all open-source service providers offer excellent technical support.
- It can be risky in the long run because the service provider may shut down after a few years. Open-source vendors are simply far less financially stable compared to established commercial vendors.
What Are the Advantages of ERP Systems?
ERP systems can help businesses of any size, from startups to Fortune 500 companies. Here are the advantages they can offer:
Reduced Operating Costs
An ERP system allows companies to save on costs and even eliminate certain expenses. For one, deploying an ERP removes the need for implementing different types of software for each department. You can do away with spending on additional licenses to use other enterprise software.
You can also automate business processes via an ERP. Automation alone can save you time and effort, reducing errors and preventing data re-entry, which can be costly to fix.
Moreover, ERP software can help your business become more efficient. Unified business functions help your company complete more tasks in fewer production hours. Lastly, your team can focus more on revenue-generating activities because the ERP platform already automates some administrative work.
Transparency of Workflows
ERPs not only set up a centralized database, but they also make your workflows visible for your team to see. Workflow transparency is vital in any business because it allows you to track how your departments are doing.
This transparency is also beneficial to your departments. They’ll know how to access the right documents to help them do their jobs. Collaboration becomes easier when every team member is on the same page.
Accuracy in Reporting and Analyzing Business Data
By centralizing your database, an ERP system allows you to generate more accurate and timely reports. You can even use the ERP to create customized reports for specific purposes. You can make accounting and budget reports, order management charts, expense ledgers, key performance indicators (KPIs), and many more.
You can also use an ERP solution for predictive analytics. Most platforms already come with data tracking and collection capabilities. Plus, you can automate advanced analytics to spot trends and patterns.
More Informed Business Decision-Making
One of the things an ERP system does best is organize your business data. Since you can easily access, collect, and analyze data, you can make the right decisions for your business.
The latest ERP systems usually come with business intelligence features. They not only offer advantages in financial reporting, but they can also provide insights into customer behavior, conversion rates, retention rates, and inventory turnover, among other things.
Compliance with Industry Standards
It’s easier to prove compliance with an accurate data tracking and management system. An ERP platform does precisely that for your business.
You can also configure the ERP to establish standards within your organization. A good example is setting up specific criteria for creating and storing documents.
Moreover, automation via ERP gives your team enough time to meet all compliance requirements.
Enhanced Risk Management
There are many ways ERP systems can mitigate risks in business. For one, it minimizes human error. At their worst, employee mistakes can impact your revenues and stain your brand reputation.
An ERP also lets you implement robust internal controls. These can help your business reduce the risk of non-compliance and even fraud.
And there’s the matter of data security, which we’ll discuss in detail in the next section.
Increased Data Security
An ERP system also doubles as a platform to ensure and enforce data security. ERPs today employ encryption methods to protect data against unauthorized access.
Cloud-based ERPs have an extra protective layer. They store and distribute data across several servers in multiple locations.
Data backups are also the norm for ERP solutions. You can still recover lost data due to natural causes or criminal intentions.
Fostering Inter-Department Collaboration
An ERP can remove communication barriers between departments. A singular platform allows your team to access the same data and collaborate more smoothly.
ERPs can also eliminate geographic barriers. With an ERP platform, collaborating with another office location is as easy as working with another department within the same building.
Scalability to Expand or Streamline
With expansion comes greater usage and an increase in the amount of data. A sound ERP system can accommodate such incremental changes.
As the business grows, its functions and processes will also evolve. Because today’s ERPs come with built-in customization, you can add new functionality to suit your changing business needs.
Customizable Features
You can take full advantage of an ERP system’s customizable features to make your operations more efficient.
Your business may have certain functions that have specific requirements. The good news is you can customize an ERP’s existing features to meet those needs.
Customization’s advantages go well beyond efficiency. A customized ERP can also give your company an edge over your competitors. In business, that edge could spell the difference between gaining profits and incurring losses.
Boosting Partner and Customer Relationships
ERPs can give insights into which of your existing partners are helping or hurting your business. Through data analysis, you can determine if this specific service provider or supplier is boosting your efficiency or slowing your operations down.
You can also use the ERP system to understand customer needs better. It gives you access to data on buying habits and shopping preferences. It can even tell you which orders will come in during a specific time of year.
Disadvantages of ERP Systems and How To Overcome Them
Despite their many advantages, ERP systems are far from perfect. If you’re planning an ERP project, you need to be aware of ERP’s potential drawbacks.
The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Can Be Too High
Some ERP systems can require a significant financial investment. Moreover, ERP consultants can sometimes command a high fee.
How to overcome this challenge: You can explore SaaS ERP solutions that only require you to pay a fee. And as mentioned before, you can also get an open-source ERP system, which shouldn’t hurt your finances. Finally, you can use tools to compute your ERP cost projections over a one or two-year period. You should be able to know in advance which ERP will suit your budget.
Steep Learning Curve
ERPs come with user-friendly UIs, but when applied to business (wherein mistakes can be costly), they may require training. And the more complex the business function, the higher the ERP training needed.
How to overcome this challenge: Prepare your team, especially those using the ERP the most. It’s best practice to assemble an ERP project team. It should consist of administrators and at least one representative from each department.
Data Conversion Is Expensive
Centralizing data is costly, especially if legacy systems and old directories are involved. Data conversion will not only incur expenses but will also take time, effort, and storage space.
How to overcome this challenge: Create a data conversion plan to define the data conversion parameters (i.e., which data to convert, and where to retrieve them). You can start with the essential data first, but you need to ensure that it’s clean data. That’s why it’s necessary to conduct a data conversion test. It should tell you if your data is ripe for conversion.
High Maintenance Costs
On-premise ERPs tend to have higher maintenance costs. After all, they are set up in-house, so you’ll need a capable IT department to manage and maintain them for years.
How to overcome this challenge: Go for cloud-based ERP solutions instead. Maintenance costs can be more predictable with cloud ERPs because they’re part of the monthly or annual fees you pay.
It Won’t Fix Problems Inherent in Business Processes and Policies
ERP systems can offer many benefits for businesses. But it can’t always fix everything. So if you have pre-existing process and policy issues, an ERP is not a 100-percent solution.
How to overcome this challenge: Implementing an ERP system does present an excellent opportunity to detect and fix your process and policy issues. Many companies change how they do things internally before or during ERP implementation. By embracing ERP, they welcomed the process of improving from within.
Stages of ERP Implementation
You can execute a successful ERP system implementation by following these seven key steps.
Planning and Analyzing Requirements
Creating a detailed plan or requirements document should provide a roadmap for an effective and efficient ERP software implementation.
In formulating this plan, you should examine your existing business functions and identify those that need improvement. Also, don’t forget to zero in on the roadblocks that cause inefficiency in your operations.
Choosing the ERP Systems Provider
Use the insights you gained from your requirements analysis to choose the ERP service provider that will meet your specific needs.
Coordinate with your systems provider to select the best ERP deployment model for your business. Again, remember that the more you define your requirements, the better your partner can collaborate with you in selecting the right ERP solution.
Designing the ERP
Map out current workflows that the ERP system will support. Note that some business functions may remain intact while others must change.
You will also need to figure out the customizations during the design stage. There’s a difference between what you want and what is realistic. Work with your ERP systems provider in identifying which customizations are “must-haves” versus those that are “nice to have.”
Configuring the ERP
Also known as the development stage, in-house or external ERP experts will start configuring the ERP platform according to your requirements.
ERP configuration will also involve data migration. While configuration and migration are ongoing, you can start gathering materials for training. Lastly, begin coordinating with your department heads to set training schedules.
Testing the ERP
ERP testing is vital because it lets you check if your ERP system will meet all business requirements and technical and functional specs.
Testing the ERP system may involve various types of tests. It may include functional testing, integration testing, performance testing, security testing, and regression testing.
Deploying the ERP
When deploying the ERP system, you can hire an ERP system integrator.
One advantage of getting system integrators is their experience with different ERP platforms. They are also up-to-date on recent ERP developments, trends, and approaches.
A system integrator will not only smoothen the ERP implementation process. They can also fast-track training, oversee ERP testing, and serve as an objective IT expert unaffected by office politics.
Providing Continuous Support
The work doesn’t stop at the ERP deployment stage. The users of the ERP system will still need ongoing support after implementation.
Providing continuous support may involve additional training, rolling new features out, and adjusting configurations. It will also include security patches and updates.
Conclusion
Enterprise resource planning systems (ERP systems) help you manage and unify all your business functions. With a single ERP system, you can make your operations more efficient and your employees more productive,
An ERP system can provide many benefits for your business. It reduces costs, makes workflows transparent, creates accurate data reports, improves data security and risk management, and helps in regulatory compliance.
FAQs on Enterprise Resource Planning Systems
What Is the Difference Between ERP and CRM?
Both ERP and CRM can benefit businesses, but they have fundamental differences. An ERP system integrates all your business processes into one unified system. Meanwhile, a CRM or Customer Relationship Management lets you manage how your customers transact or interact with your business. Some ERP systems may include a CRM component.
Can ERP Systems Be Hacked?
Although ERP systems have security features, they are still hackable. ERPs that are most vulnerable to cyberattacks are those that use legacy technologies. Examples of legacy tech that are easy to hack include clear text exchanges and file transfer protocol (FTP).
Here are other factors that could weaken an ERP system’s security:
- Delayed updates
- Failure to comply with industry standards
- Mismanagement of access rights
- Inadequate training in data security practices
We’re BIT Studios!
At BIT Studios we specialize in designing, building, shipping, and scaling beautiful, usable products with blazing-fast efficiency